当社の個人情報保護方針&クッキーポリシー
当社のウェブサイトではクッキーを使用し、ユーザー様のオンライン体験を向上させております。このウェブサイトを立ち上げたときに、クッキーはお使いのコンピュータ上に配置されます。インターネットブラウザの設定を通して、個人的なクッキーの設定を変更できます。
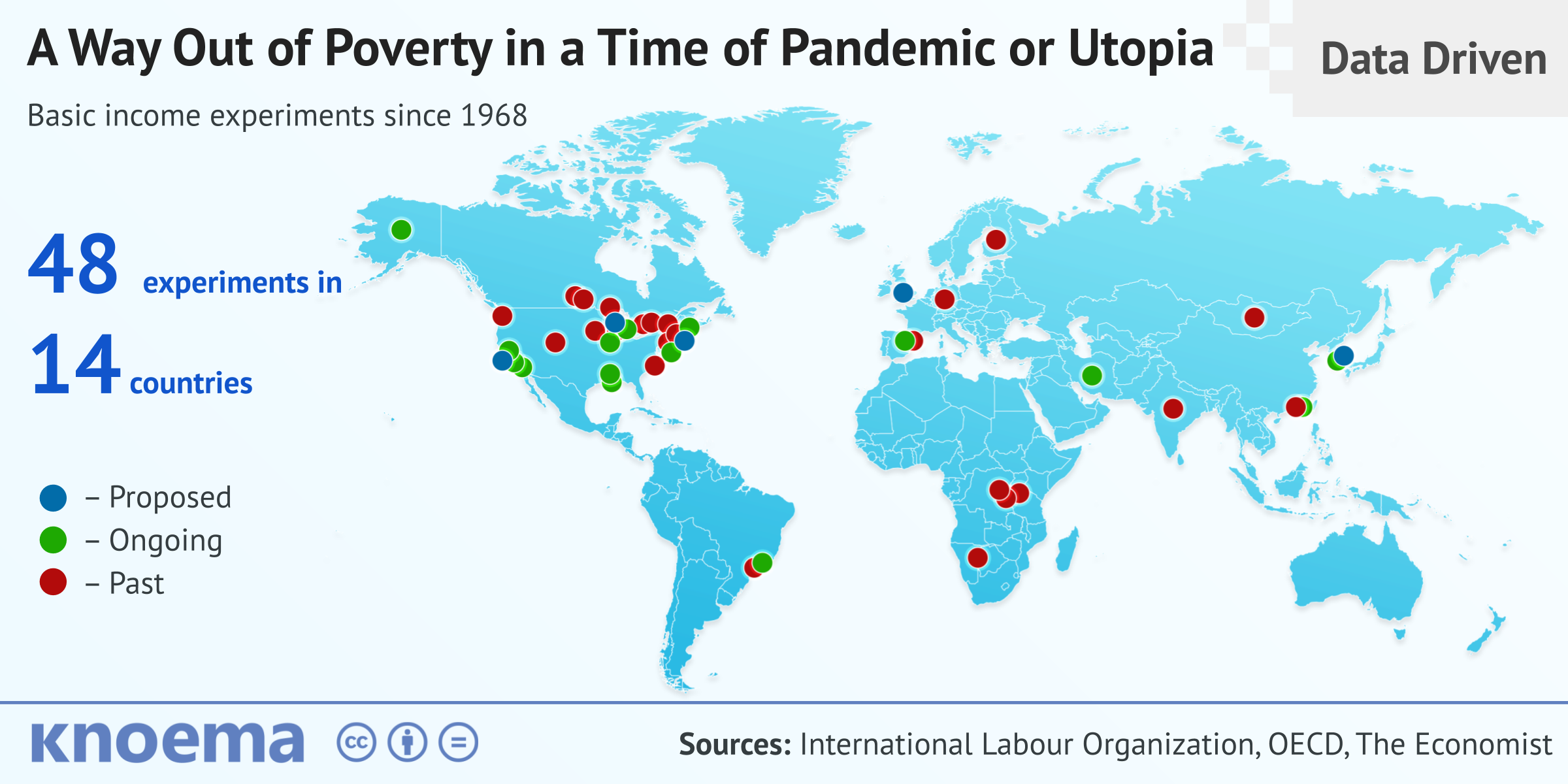
個人情報保護方針(23 September 2020) Sir Thomas More introduced the concept of basic income* in Utopia back in 1516. It's a simple concept: Eliminate poverty by guaranteeing a basic level of income. The New Jersey Income Maintenance Experiment (1968-1972) was the first basic income experiment and has since been followed by more than 40 experiments across 14 countries, including 16 ongoing, and another 5 experiments planned for 2020 or later. From an experimental perspective with small groups of participants (as opposed to whole economies), the data demonstrates that basic income helps to eradicate poverty and without many of the anticipated negative effects.
So, while the idea of basic income may have appeared on the public stage more than 500 years ago, we had to wait until the 20th century for broad political and public discussion to trigger experimentation globally. The findings from these experiments could not be more relevant than in this time of COVID as governments worldwide evaluate new policy approaches for economic stimulus and general resilience to avoid future economic slowdowns from shocks like the COVID-19 pandemic.
*Definition: Basic Income is a periodic cash payment unconditionally delivered to all on an individual basis, without means-test or work requirement. BIEN
Live data and insights on Coronavirus around the world, including detailed statistics for the US, EU, and China — confirmed and recovered cases, deaths, alternative data on economic activities, customer behavior, supply chains, and more.
(27 March 2020) The force that is 'global social exclusion' is becoming a fatal event for some businesses that rely on in-person labor force and customers, while for others it is a chance for rapid growth and development of new services lines. As the coronavirus infections curve worldwide has shifted over recent weeks to become still steeper, entire companies have begun switching to remote work operations. Many industries, such as air travel, tourism, and retail are undergoing rapid business model adjustments to soften the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Below we share another...
Prosper Insights & Analytics has 18 years of experience producing market leading monthly survey-based research of consumers' overall confidence. In its most recent survey, Prosper asked consumers about their concerns with regard to the coronavirus pandemic and the related cancellation of major events. You can explore Prosper's latest findings in depth below, but we'll give the spoiler: 82% of US consumers expressed one form of concern or another and believe that they will somehow experience direct consequences of the pandemic. Moreover, for the first time in six months there is...
(3 February 2020) As the World Health Organization has elevated the global public health threat level posed by the coronavirus to 'very high' (China) and 'high' (rest of the world), global economic health is also beginning to suffer. The number of people affected by the coronavirus globally may seem relatively small — just over 14,632 deaths and 335,953 people infected — yet without containment, especially to avoid spread to countries with weaker healthcare systems, the human (and economic) toll could rise rapidly into a full global epidemic. As the second-largest economy in the...
(Published - April 20, 2020. Data updated - May 26, 2020) A growing number of social protests have swept the United States this month in opposition to measures imposed to slow the spread of the coronavirus. Protesters seek policy changes to restart state economies and are providing fresh political opportunities that President Trump has reframed via Twitter as an imperative to 'LIBERATE' US states from COVID-19 restrictions. In the week spanning 13-19 April 2020, we estimate that approximately 9,000 people left their homes to participate in protests and demand state governors relax...
当社のウェブサイトではクッキーを使用し、ユーザー様のオンライン体験を向上させております。このウェブサイトを立ち上げたときに、クッキーはお使いのコンピュータ上に配置されます。インターネットブラウザの設定を通して、個人的なクッキーの設定を変更できます。
個人情報保護方針